Buy ePassport Online
An ePassport, also known as Electronic Passport, Digital Passport, Biometric Passport, or e-passport is a paper-based passport that embeds a contactless smart card chip and an antenna.

The contactless smart card chip is connected to the antenna – made of multiple loops of thin copper wire – that is used for both communication and power. The contactless chip and the antenna works at an operating frequency of 13.56 MHz and shall comply with the ISO/IEC 14443-1 specifications. http://counterfeitnote.com/2018/01/23/online-passport-application/Purchase Biometric Passports Online
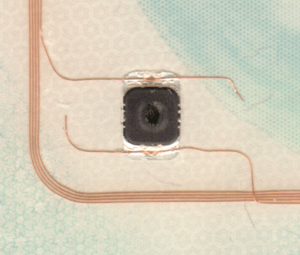
The contactless chip and the antenna are packaged in a layer structure called ePassport Inlay. There are two types of ePassport Inlays available in the market:
- Single Layer – one side of the chip module / antenna is not covered and they have a thickness of about 300 ∼ 400 μm
- Double Layer – the chip module / antenna are encapsulated into a sandwich-like structure and they have a thickness of about 400 ∼ 500 μm.
 The sheets that protect the chip module and the antenna can be made of polyester(PET), polycarbonate, Teslin or other synthetic material. The dimension of an ePassport inlay is normally the same or slightly smaller of a passport page and can be embedded:
The sheets that protect the chip module and the antenna can be made of polyester(PET), polycarbonate, Teslin or other synthetic material. The dimension of an ePassport inlay is normally the same or slightly smaller of a passport page and can be embedded:
- into the ePassport cover, this is called “e-cover”. This was the first method used in the industry because in 1998, when the first ePassport was launched, the thickness of the chip was such that the only suitable place to host it was the multi-layer cardboard cover. Al tough this is still the most popular method for chip embedding, forensic crime experts have noticed possibility to swap the cover with a fake one or – another possibility – to get a genuine cover (with its chip embedded) and collate it to a fake passport.
- into the polycarbonate ePassport Data Page, this is called “e-datapage”. This method is growing popularity in recent years primarily driven by the new chip packaging available that are thick as low as 200μm. This option does offer the highest level of security both in terms of linking the holder printed information with the electronically stored information and physical attacks.

- as middle page of the ePassport booklet. This has – by far – the lowest production cost and is not widely popular.

When the inlay is embedded into the passport cover, the chip and the antenna are not visible to naked eyes. Buy ePassport Online
The specification of the ePassports are defined by the International Civial Aviation Organization (ICAO) in the document series called Doc 9303 – Machine Readable Travel Documents. Within the ICAOnaming the ePassport is referred as Machine Readable Travel Document or MRTD. In some publications the ePassport is also referred as eMRP (Electronic Machine Readable Passport).
ICAO have designed a symbol have been designed to visually distinguish an ePassport. The “Chip Inside” symbol, also known as Electronic Machine Readable Travel Document (eMRTD) must be printed on the top or on the bottom part of a ePassport front cover.

The optional data stored into the ePassport chip include:
- Other names
- Place of Birth
- Address
- Telephone Number(s)
- Profession
- Title
- Personal Summary
- Proof of Citizenship
- Other Valid Travel Document(s)
- Other Person(s) included on MRTD
- Endorsement/Observations
- Tax/Exit Requirements
- Image of Front of MRTD
- Image of Rear of MRTD
- Name of Person(s) to Notify
- Contact Details of Person(s) to Notify
- Fingerprint
- Iris scan
- Country-specific Forensic Feature, example booklet lot number printed on microtext on the cover.

As of time of writing the vast majority of Issuing Authorities uses only Face Photo as means of identification while few uses both face and finger.
To avoid that anyone with a ePassport Reader could read and steal sensitive personal information from the contactless chip, two set of security features were introduced by ICAO: Buy ePassport Online
- Basic Access Control (BAC) that is a mechanism that protects the contactless chip from being read without direct access and ensures that information exchanged with the reading device is encrypted. For instance, an ePassport that implement the BAC cannot be read while is kept in a travel bag. In order to access the data stored on the contactless chip of the ePassport, first is necessary to scan/read the Machine Readable Zone (MRZ) of the document. Based on this data, an individual access key for each passport is computed, which is used by the ePassport reader to authenticate itself to the chip. This means that the ePassport reader proves to the chip it has optical access to the passport. The contactless chip transmits a random number to the ePassportreader for this purpose. Then the ePassport reader encrypt this number using the access key and then transmit it back to the contactless chip. The chip then checks if the random number has been encrypted with the right access key. If this is the case, the contactless chip allows the ePassport reader to access the data.
- Extended Access Control (AEC). ICAO defines that chip must contain chip-individual keys, must have processing capabilities and additional key management for mutual authentication mechanism is required. The actual implementation is left to the individual implementing States.

The ePassport electronic holder’s data are written into the contactless chip during the issuance process performed by the Issuing Authority and cannot be modified. This means that when in the field an ePassport can only be read and no-one, even the issuing authority can modify its content.Buy epassport online

ICAO is currently working on the next evolution of the ePassport called Logical Data Structure Version 2 (LSD2) where there will be an optional read-write function in order to accommodate electronic record of Travel Stamps, Visas and additional Biometric information. In addition, LDS2 will further protect the ePassport against counterfeiting, copying and unauthorized reading or writing.





 There are many advertisements on the internet from people selling fake passports, but “fake” usually really means “novelty” which means its not an original passport but more like some fantasy passport.
There are many advertisements on the internet from people selling fake passports, but “fake” usually really means “novelty” which means its not an original passport but more like some fantasy passport. 

